Share this
What does biodegradable sugarcane material mean?
Biodegradable sugarcane utensils – sos –
Why biodegradable sugarcane utensils? A plastic bag needs 10-20 years to dissolve in the sea, a plastic glass 50 and a plastic bottle “only” 450 years.
Plastics, or synthetic polymers, are widely used both because of their mechanical and thermal properties – mainly their durability and resistance to various types of corrosion – and because of their low price.
Their use in short-lived applications, such as product and food packaging (which accounts for the bulk of waste, almost 1/3 of the volume of waste), created the big problem of environmental pollution and lack of disposal space – a scourge of the era.
From studies carried out it became known that at the end of the 20th century the production of plastics had reached 130 million tons per year. Proportionally, each person uses about 100 kg of plastic per year. Common plastics remain in the environment for hundreds of years due to the fact that microorganisms found in soil are generally unable to break down a polymer chain composed entirely of carbon atoms that does not exist in nature. For this reason, there was a need to replace common plastics with new, innovative materials from sugar cane that have the same functionality, while being more environmentally friendly.
Biodegradable – Polymeric materials
In recent decades, new polymeric materials have appeared which have the property of breaking down in the environment in a short period of time. The so-called biodegradable polymers.
*At Eco care we produce biodegradable tableware from sugar cane. Discover more about us here.
Biodegradation of plastics
Biodegradation of plastics does not depend only on the raw material of their production, but on their chemical structure and composition. For this reason, biodegradable plastics can be derived from natural or synthetic polymers. “Environmentally degradable polymers” are divided into categories according to their breakdown mechanism, which are as follows:
• Biodegradable
• Compostable
• Hydrobiodegradable
• Photodegradable
• Photobiodegradable
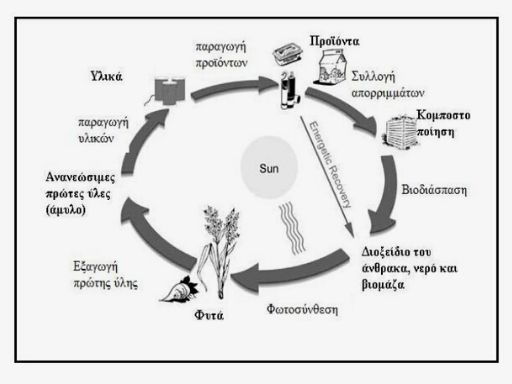
Biodegradable polymers break down under specific fermentation conditions into carbon dioxide, water and biomass.
The compostable polymers are placed in the composting bin together with the rest of the organic waste to create fertilizer (compost). Hydro-biodegradable polymers break down through hydrolysis and are those that contain starch or its derivatives in a high percentage. Photodegradable polymers only break down under the influence of solar radiation.
Photo-biodegradable polymers, in contrast, do not require the continuous presence of light. Their technology is based on the addition of a small amount of “disintegrant” which, when introduced into the plastic during the production process of the raw material, changes the behavior of the plastic. Photo-biodegradable plastics, after being exposed to the sun for some time, even with burial, will degrade with the help of bacteria and fungi as previously the “decomposer” has broken down the macromolecules of the plastic into smaller ones.
Biodegradable polymers are degraded by natural agents, primarily in the presence of microorganisms, and may involve processes such as dissolution in water. The degradation environments of photodegradable and biodegradable polymers differ and for this reason they do not belong to the category of biodegradable polymers.
The development of biodegradable polymers, i.e. polymers that usually come from renewable raw materials and are broken down after their disposal by microorganisms in the environment, is an alternative solution to the applications of common plastics, since they have similar physical and mechanical properties to conventional plastics and in addition they provide a solution to the problem of environmental pollution, saving landfill space and de-addiction from oil.
Biodegradable polymers, unlike common plastics, break down over time into carbon dioxide, water and biomass.
All Eco care products are biodegradable and compostable. In 45-90 days they break down into carbon dioxide, water and biomass, in the composter or landfill (if it meets the right humidity and temperature conditions).
•❯ Earth Loves You, Love it Back | Eco care!
